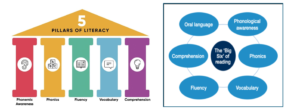
Reviews into reading consistently identified 5 key components necessary for successful reading acquisition.
Reviews: (attached for your reference)
- The National Reading Panel (USA),
- The Rose Report (UK),
- The Rowe Report (AUS).
Research has emphasized the interconnectedness of these components and sequence in which they occur for reading. The 5 Pillars of Reading is also referred to as The Big Six, which additionally has Oral Language at its core.
Reading is a complex process that involves the integration of all of the following components. None of these are more or less important, and all must be explicitly taught in every classroom.
Attached for your reference is Deslea Konza”s paper on Teaching Reading: Why the “Fab Five” should be the “Big Six”
Phonemic awareness: the ability to identify and manipulate the smallest units of sound (phonemes)in spoken words. Phonemic awareness falls under the umbrella category of phonological awareness, which includes the understanding of the broader categories of sound, including words, syllables, and onsets & rimes. Although the National Reading Panel (NRP) identified “awareness” as the goal, subsequent research specifically on orthographic mapping has yielded an understanding that “phonemic proficiency” is both critical to and a result of orthographic mapping, and that it continues to develop throughout primary school (Kilpatrick, 2019).
Phonics: is a way of teaching letter-sound correspondences (phoneme-grapheme representations) and their use when reading (decoding) and spelling (encoding).
Fluency: the ability to read with accuracy, automaticity(rate) and prosody (expression).
Vocabulary: the understanding of words and word meanings,
Comprehension: the understanding of connected texts. It is considered an ‘essential element’ of reading but is more accurately referred to as the ‘goal of reading’. Reading Comprehension is the result of mastering and integrating all components of effective instruction.
Oral language: provides the foundation for reading and writing.
The Simple View of Reading and Scarborough’s Reading Rope provide frameworks for understanding how the components are interconnected and lead to skilled reading comprehension.
In Unit 6 we will be looking at how you might structure these in your literacy block but first we will delve a little deeper into the science.
Watch the following video in which Hugh Catts discusses the 5 Pillars of reading.
https://www.youtube.com/embed/4b2e3nKRyJA?feature=oembed

Ep.177: The Five Pillars of Reading with Hugh Catts
Associated Resource and Review Links:
The Rose Report (UK) Independent Review of the Teaching of Early Reading (UK) – The Rose Report – Learning Difficulties Australia Inc. [ARCHIVED CONTENT]
The National Reading Panel Report (2000 USA) National Reading Panel – Teaching Children to Read: An Evidence-Based Assessment of the Scientific Research Literature on Reading and Its Implications for Reading Instruction
THE NATIONAL READING PANEL REPORT: Practical Advice for Teachers
