What causes poor comprehension
There are four main reasons a student has poor reading comprehension
The student may have:
- Underlying reading disability
- Underling language disorder
- Working memory deficits
- Inadequate instruction
Through adequate assessment to identify underlying causes, reflection on instruction, practice and intervention, and a supportive network (MTSS), educators are able to of identify individual student needs and collectively design and implement effective high-quality interventions. However, the implementation of high-quality Tier 1 evidence-based reading programs and instructional practices for all students is our first point of call.
The urgency of early intervention to address underlying causes has been highlighted by the findings of reading research. For example:
“… children’s level of reading achievement is determined early in their school experience . . . By third grade, the level of reading ability that children have attained is likely to remain relatively stable; it is difficult to escape a pattern of failure that has lasted through a large part of elementary school.”
Spira, E., Bracken, S., & Fischel, J. (2005). Predicting Improvement After First-grade Reading Difficulties: The Effects Of Oral Language, Emergent Literacy and Behaviour Skills. Developmental Psychology., 41(1), 225-234.
“Year 3 students who perform below learning expectations are at a high risk of continuing to perform at that level outcomes.” (p. 5) Learning. Australian Education Research Organisation. throughout their schooling. This shows the importance of early assessment of student progress against expected
Williams, L., Groves, O., Wan, W.-Y., Lee, E., & Lu, L. (2023). , Outcomes of Students with Early Low NAPLAN Performance “Year 3 students who perform below learning expectations are at a high risk of continuing to perform at that level outcomes.” (p. 5) Learning. Australian Education Research Organisation.
Listen to Jenny Peach, Qld Department of Education’s Speech Language Pathologist, discuss reading difficulties and how schools can meet the needs of students with reading difficulties.
https://youtu.be/l4K7CqMfuXw?si=VsA7kxaULZ2KO-qK
Qld Dept of Ed Partners in Learning videos for educators, families and home tutors – YouTube
Subtypes of Poor Reading
For a deeper dive read Reading Rockets explanation of the Types of Reading Disability | Reading Rockets
by Louisa Moats and Carol Tolman, authors and creators of LETRS Language Essentials for Teachers of Reading and Spelling.
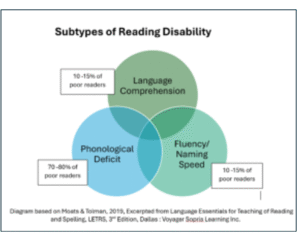
Diagram informed by Moats, L, & Tolman, C (2009). Excerpted from Language Essentials for Teachers of Reading and Spelling (LETRS): The Challenge of Learning to Read (Module 1). Boston: Sopris West.
The Simple View of Reading (SVR) Gough & Tunmer (1986)

Gough and Tunmer’s, Simple View of Reading (1986) can explain reading competency across all ages and grade levels and can help determine a student’s reading strength and / or weaknesses, and guide educators towards intervention.
Reading comprehension is conceptualised as a product of both components of the equation, without one component, reading comprehension competency will not be achieved. Simply put, reading comprehension is underpinned by prior knowledge of these two broad sets of abilities. Whilst it looks simple, Scarborough’s Reading Rope (2001) illustrates the complexity behind the equation.
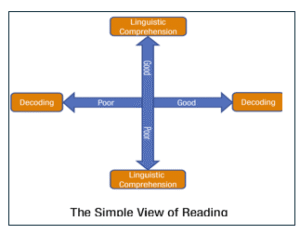
Gough, P. B., & Tunmer, W. E. (1986). Decoding, Reading and Reading Disability. Remedial And Special Education, 7(1), 6–10. Hoover, W. A., & Gough, P. B. (1990). The Simple View of Reading. Reading & Writing; An Interdisciplinary Journal, 2, 127-160.
How Does the Equation Work?
If one or both sides of the equation are missing or diminished, then reading comprehension will suffer.
For example, the following represent how the equation works.
WR X LC = RC
1 X 1 = 1 Good Reading Comprehension
0 X 1 = 0 Poor Reading Comprehension – Word Reading Deficit
1 X 0 = 0 Poor Reading Comprehension – Oral Language Comp Deficit
The following Illustrates how diminished levels of WR and LC impact on Reading Comprehension
WR X LC = RC
0.4 X 0.4 = 0.16 Poor Reading Comprehension
0.7 X 0.7 = 0.35 Poor Reading Comprehension
0.7 X 1 = 0.7 Poor Reading Comprehension
For beginning readers, decoding (Word Recognition) is a better predictor of their reading success, but once children have developed a level of automaticity of the foundational skills of Word Recognition (WR), the skills under Language Comprehension (LC) become more important for reading success.
Simple View of Reading 2D Quadrant
The Simple View of Reading (SVR) predicts 4 different types of reading (see diagram below)
The equation helps educators pinpoint students’ strengths and weaknesses in reading. This equation allows teachers to identify the possible reading difficulties a student may have i.e. dyslexia, hyperlexia, and mixed disabilities.
- Students who have poor skills on both sides of the equation, which David Kilpatrick calls “mixed types” are the most common type of reading difficulty.
- Students with dyslexia or poor word reading and adequate language comprehension (less common)
- Students that are hyperlexic often referred to as “word callers” (least common)
Understanding the different reader profiles in a classroom helps informs planning, instruction and intervention.
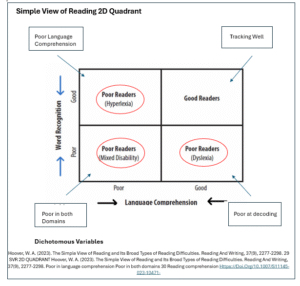
Gough, P. B., & Tunmer, W. E. (1986). Decoding, Reading and Reading Disability. Remedial And Special Education, 7(1), 6–10. Hoover, W. A., & Gough, P. B. (1990). The Simple View Of Reading. Reading & Writing; An Interdisciplinary Journal, 2, 127-160.
Hoover, W. A. (2023). The Simple View of Reading and Its Broad Types of Reading Difficulties. Reading And Writing, 37(9), 2277-2298. 29 SVR 2D QUADRANT
Hoover, W. A. (2023). The Simple View of Reading and Its Broad Types of Reading Difficulties. Reading And Writing, 37(9), 2277-2298.
Poor in language comprehension Poor in both domains 30 Reading comprehension Https://Doi.Org/10.1007/S11145-023-10471-
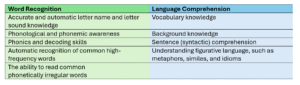
Simple View of Reading Skills
So, let’s look at a list of the skills included within the SVR framework.
As the SVR 2D Quadrant has illustrated, a student with poor reading comprehension may need intervention in a number of these areas. The answer to which support is required may lie amongst the acquisition of WR and LC skills.
Screening and diagnostic assessments provide teachers with the specific information required to tailor their teaching to meet the individual demands of the students in their care.
Helping poor comprehenders – Five from Five